Tax Planning for Salaried Individuals
- Posted By Amritesh
- On September 19th, 2019
- Comments: 4 responses
Tax Planning for Salaried Individuals is very important as it not only helps in reducing the tax outgo but also encourages investment towards secured future. Salaried Individuals may avail the tax benefits to significantly reduce their tax outgo. Furthermore, some of the salary components are partially or fully exempted from tax, subject to fulfilment of the conditions laid down for the same. Standard Deduction is one of the benefits available to the Salaried Class to reduce the tax liability.
Salary Components and Income Tax Implications
Contribution to Statutory Funds: Tax Planning for Salaried Individuals
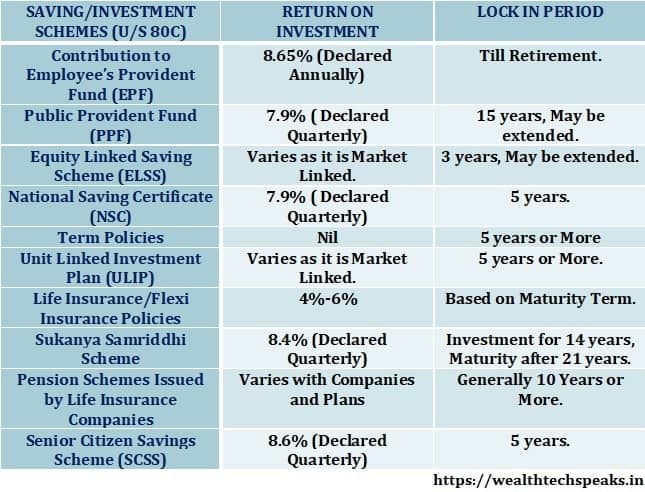
Employees Provident Fund (EPF): Contribution towards EPF is eligible for deduction under section 80C up to the maximum limit of Rs 1,50,000/-. Currently, EPF fetches an interest of 8.65% on the contribution.
Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF): Individuals may also make additional contribution to EPF on voluntary basis. Apart from 12% Statutory Deduction, Employee may request his/her employer to contribute further 88% of the Basic to EPF. However, Employer is not required to match the additional voluntary contribution.
Contribution and Exemptions: Tax Planning for Salaried Individuals
Tax Deductions available under the Chapter VIA
National Pension Scheme (NPS): Pension benefit plan is introduced to strengthen the Social Security Schemes in India for Citizens. Income Tax Deduction is available on contribution to NPS. Individuals may claim additional deduction up to Rs 50,000/- U/S 80 CCD (1b) on investment contribution to NPS. Deduction is also available on investment in the low cost Atal Pension Yojana as well.
Furthermore, contribution made by employer towards NPS is also allowed as deduction under Section 80CCD(2). This deduction does not have a monetary restriction, but the total deduction claimed on such contribution should not exceed 10% of the salary (14% in case of Central Government Employees).
Atal Pension Yojana (APY)
House Rent Allowance (HRA): HRA component is also eligible for deduction, in case, one is staying in rented apartment. The Tax Deduction may be calculated in the manner explained below.
Deduction from House Rent Allowance is allowed under section 10(13A), which is least of the following 3 conditions:
i.) Actual HRA received as part of the Salary
ii.) 40% of Salary, Basic plus Dearness Allowance (50% of the salary if the rented property is in Metro City i.e. Mumbai, Delhi, Chennai or Kolkata)
iii.) Actual rent paid less 10% of salary (Basic plus Dearness Allowance)
Child Education: Tax Deduction is also available for expenses incurred towards Child’s Education. Furthermore, Tuition Fee paid to School, College and University is also eligible for Deduction U/S 80C. The deduction is available for maximum of two children.
Tax Benefits on Payment of Health Insurance Premium
Medical Premium: Health Insurance Premium paid by a Tax Payer is also eligible for Tax Deductions u/s 80D up to Rs 25,000/- for self, spouse and dependent children. Deduction is further enhanced by Rs 25,000/- on medical insurance premium paid for parents (father/mother), the deduction goes up to Rs 50,000/- in case any of the parent’s age is above 60 years.
Standard Deduction: Reintroduced in the Budget 2018,Individuals get a straight away deduction from the Salary Income. This deduction is provided in lieu of benefits under Conveyance Allowance and Medical Reimbursements. Standard Deduction of Rs 50,000/- is available for the Financial Year 2019-20.
Tax Planning allows the assessee to reduce the tax liability by availing the permissible tax deductions and exemptions available under the Income Tax Act.
This article is for informational purpose only. Readers are advised to research further to have detailed knowledge on the topic. It is very important to do your own analysis and consult your Financial Advisor before arriving at any conclusion.